- + 91 989 920 79830 / 998 755 7585
- info@biomaxnaturals.com


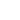
Ellagic Acid
Ellagic Acid SUPPLIERS IN MUMBAI, INDIA
Plants produce ellagic acid to protect themselves from microbiological infection and pests. Ellagic acid has antiviral and antibacterial properties.
Ellagic acid has antioxidant, anti-mutagen and anti-cancer properties. Studies have shown the anti-cancer activity on cancer cells of the breast, oesophagus, skin, colon, prostate and pancreas. More specifically, ellagic acid prevents the destruction of P53 gene by cancer cells. Ellagic acid can bind with cancer causing molecules, thereby making them inactive.
It has been demonstrated that ellagic acid causes a decrease in total hepatic mucosal cytochromes and an increase in some hepatic phase II enzyme activities, thereby enhancing the ability of the target tissues to detoxify the reactive intermediates. Ellagic acid showed also a chemoprotective effect against various chemically induced cancers.
Ellagic acid is present in many red fruits and berries, including raspberries, strawberries, blackberries, cranberries, pomegranate and some nuts including pecans and walnuts. The highest levels of ellagic acid are found in raspberries. In plants ellagic acid is present in the form of ellagitannin, which is ellagic acid bound to a sugar molecule.
Description
- Ellagic acid is a fused four-ring polyphenol.
Color/Nature
- Pure ellagic acid is a cream to light yellow crystalline solid.
Synonyms
- Benzoaric acid, eleagic acid, elagostasine, gallogen.
